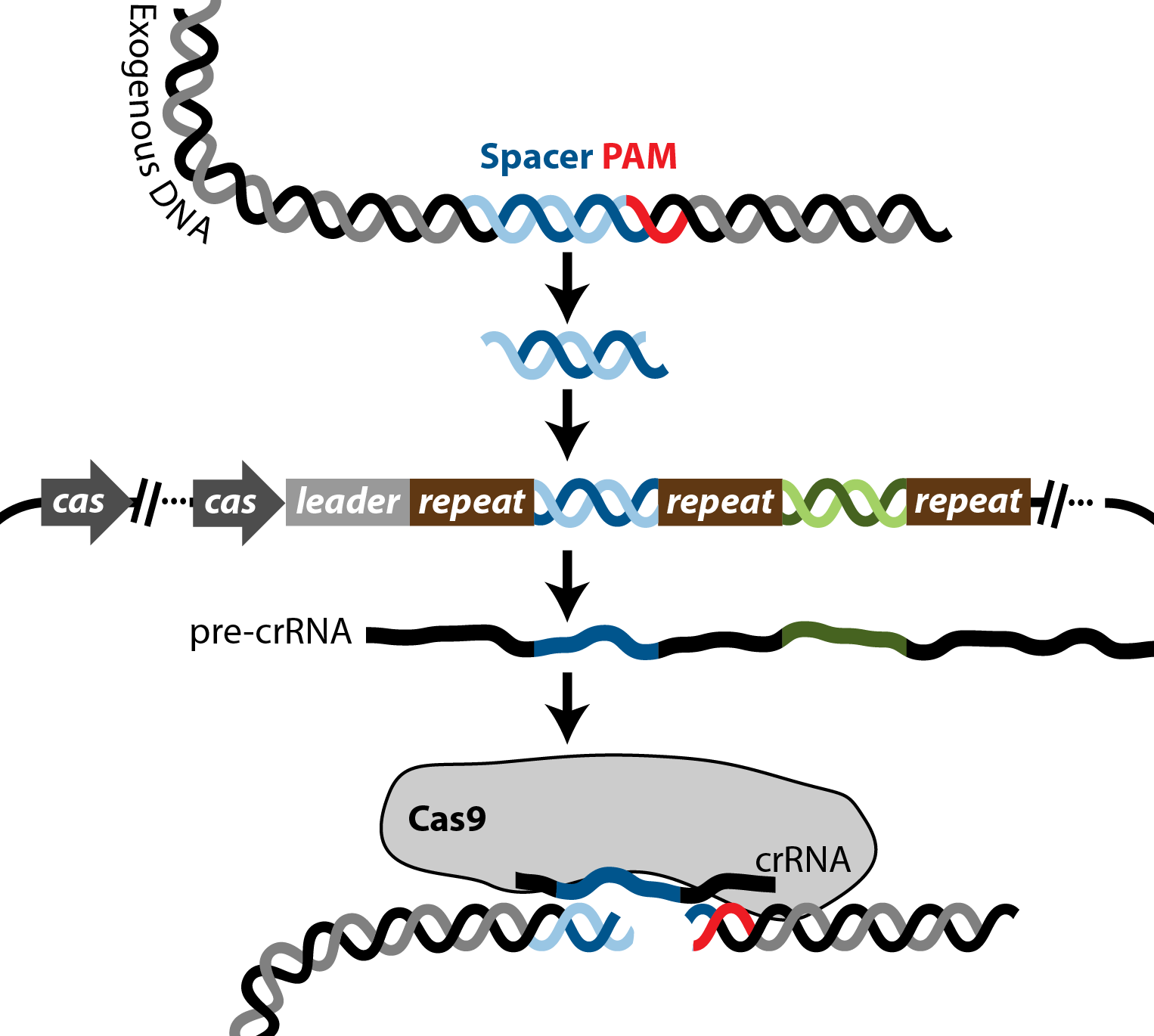
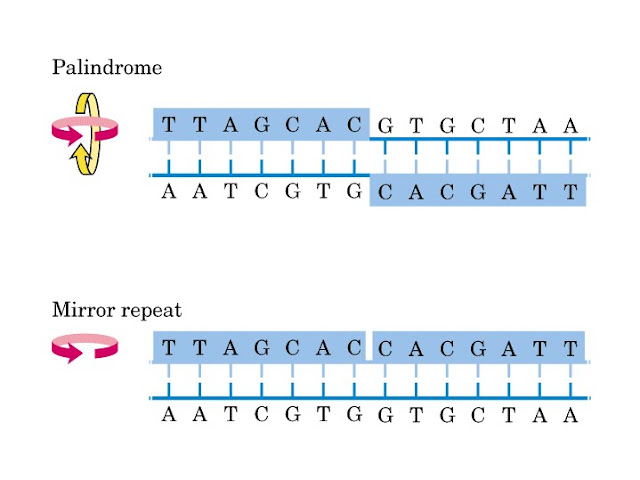
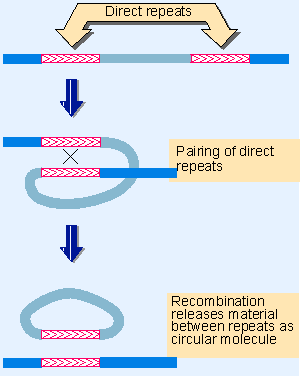
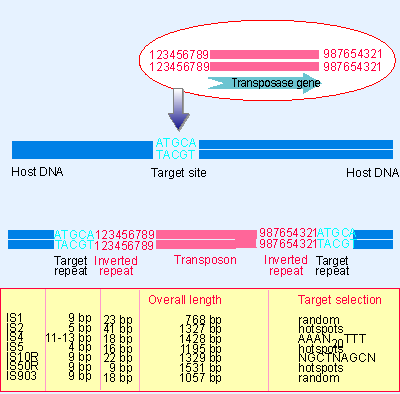
Bacterial CRISPR Regions: General Features and their Potential for Epidemiological Molecular Typing Studies

Engineering the Direct Repeat Sequence of crRNA for Optimization of FnCpf1-Mediated Genome Editing in Human Cells: Molecular Therapy

Engineering the Direct Repeat Sequence of crRNA for Optimization of FnCpf1-Mediated Genome Editing in Human Cells: Molecular Therapy

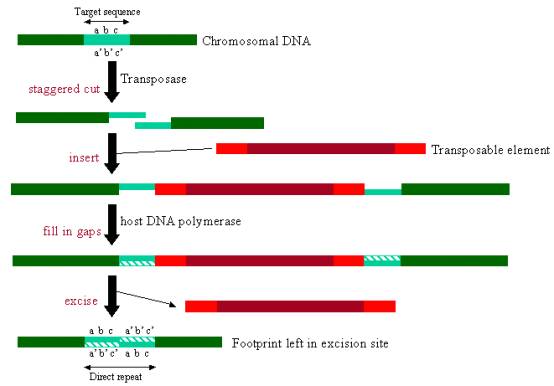
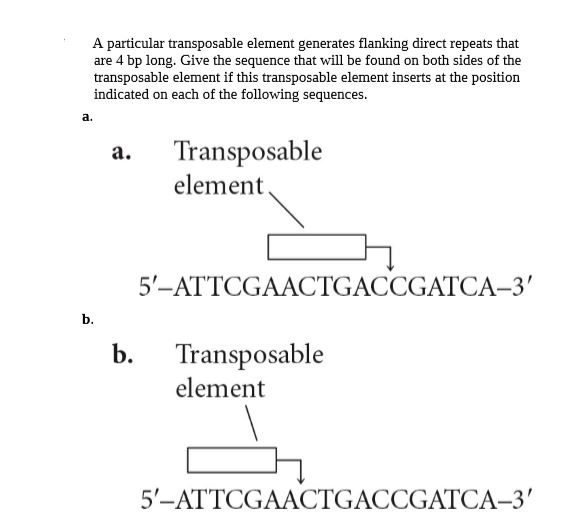
SOLVED: Question 10 0/ 4 pts Aparticular transposable element generates flanking direct repeats that are bp long: The cut that the transposase makes is staggered upstream: Give the sequence that will be

Comparison of the sequences of the three direct repeats surrounding the... | Download Scientific Diagram

Whole genome sequencing for the diagnosis of neurological repeat expansion disorders in the UK: a retrospective diagnostic accuracy and prospective clinical validation study - The Lancet Neurology
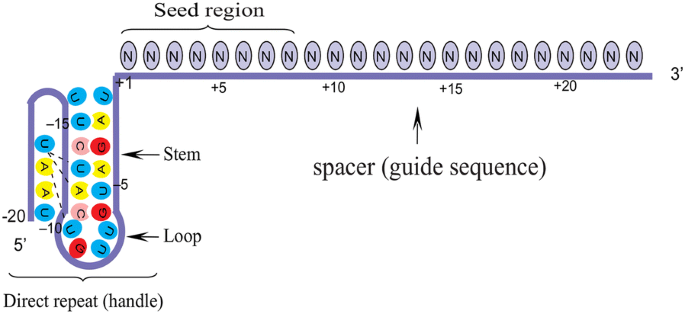
CRISPR Cpf1 proteins: structure, function and implications for genome editing | Cell & Bioscience | Full Text